Are you having trouble finding 'siadh case study'? Here you can find questions and answers about the issue.
Case Study: Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Internal secretion (SIADH) Anthony says, “This is distracted. I have lung cancer, how did I get letter a disease of the Pituitary gland?” Listing the symptoms of SIADH.
Table of contents
- Siadh case study in 2021
- Hyponatremia practice questions
- Siadh causes
- Hyponatremia case study
- Siadh headache
- Hyponatremia and siadh: a case study for nursing consideration
- Hyponatremia case presentation ppt
- Hyponatremia case study quizlet
Siadh case study in 2021
 This picture demonstrates siadh case study.
This picture demonstrates siadh case study.
Hyponatremia practice questions
 This picture demonstrates Hyponatremia practice questions.
This picture demonstrates Hyponatremia practice questions.
Siadh causes
 This image demonstrates Siadh causes.
This image demonstrates Siadh causes.
Hyponatremia case study
 This image representes Hyponatremia case study.
This image representes Hyponatremia case study.
Siadh headache
 This image illustrates Siadh headache.
This image illustrates Siadh headache.
Hyponatremia and siadh: a case study for nursing consideration
 This picture shows Hyponatremia and siadh: a case study for nursing consideration.
This picture shows Hyponatremia and siadh: a case study for nursing consideration.
Hyponatremia case presentation ppt
 This image representes Hyponatremia case presentation ppt.
This image representes Hyponatremia case presentation ppt.
Hyponatremia case study quizlet
 This image representes Hyponatremia case study quizlet.
This image representes Hyponatremia case study quizlet.
What does it mean for a person to have SIADH?
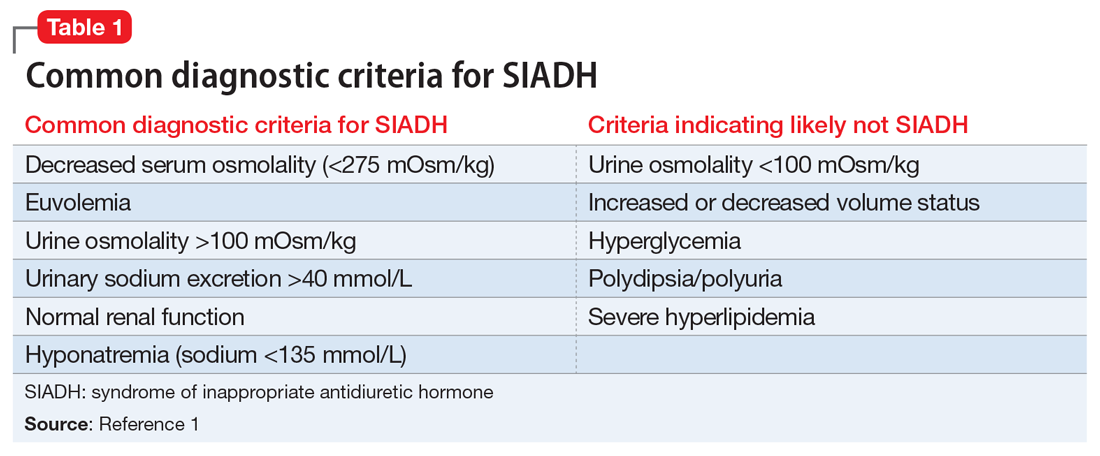
SIADH can occur secondary to medications, malignancy, pulmonary disease, or any disorder involving the central nervous system. Diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical euvolaemic state with low serum sodium and osmolality, raised urine sodium and osmolality, and exclusion of pseudohyponatraemia and diuretic use.
What are the side effects of traditional treatment for SIADH?
In at least two of the cases, the underlying cause of SIADH was impossible to reverse. Traditional treatment for SIADH with fluid restriction and demeclocycline failed, caused side effects or increased duration of hospital stay. These examples suggest a need for better treatment options.
How many cases were presented to illustrate the challenges of drug-induced SIADH?
Three cases are presented to illustrate these challenges. The first two cases had drug-induced SIADH secondary to a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (for depression) or carbamazepine (for trigeminal neuralgia). The third case had SIADH possibly secondary to bronchiectasis.
What type of medical tests should be performed to determine the cause of SIADH?
• chest X-ray if pulmonary causes of SIADH are suspected. Physical examination, including measurement of pulse and blood pressure and assessment of hydration, should also be performed to determine whether the patient is clinically hypovolaemic, hypervolaemic or euvolaemic.
Last Update: Oct 2021